1
MCQ on market and market failures
Posted by Economics Corner
on
5:05 AM
1 Which one of the following could explain a shift to the right of the supply curve for a good?
A The imposition of a tax on the good
B A new supplier entering the market
C A rise in firms’ wage costs
D A rise in the price of the good
2 Which one of the following is an example of market failure?
A Prices do not reflect the full social costs of production.
B Prices rise so that consumers cannot afford to buy all the goods that they used to purchase.
C Demand falls so that firms have to make workers redundant.
D A firm goes out of business because it cannot find a market for its products.
3 In August 2000 the World Health Organisation said that a 10% increase in cigarette prices worldwide would reduce consumption by 4% in high-income countries and by 8% in low-income countries.
The above statement suggests that
A smokers in high-income countries are twice as addicted as those in low-income countries.
B demand for cigarettes is price elastic in both low-income and high-income countries.
C income elasticity of demand for cigarettes is higher in low-income than in high-income countries.
D price elasticity of demand for cigarettes is negative in both high-income and low-income countries.
4 The diagram below shows the production possibility boundaries for Countries X and Y respectively.
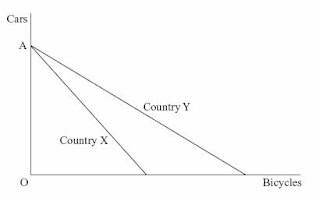
The opportunity cost of cars in terms of bicycles
A is greater for Country X than for Country Y.
B is greater for Country Y than for Country X.
C increases as more cars are produced.
D increases as more bicycles are produced.
5 The National Grid is a system which distributes electricity throughout Britain. It is currently a monopoly. A possible advantage of this monopoly position to electricity customers is that
A a lack of competition in the electricity distribution industry encourages lower prices.
B the monopolist is able to offer lower prices to customers because it can exploit economies of scale.
C by charging high prices, the monopolist is able to ensure an efficient allocation of resources.
D there will be no need for innovation and invention in the electricity distribution industry and so customers can enjoy lower prices.
6 To benefit from specialisation, it is necessary
A to have an efficient means of exchanging goods and services.
B for labour productivity to be high.
C for the production possibility boundary of the economy to be moving outwards over time.
D for significant economies of scale to be gained in all industries.
7 Which one of the following statements involves a value judgement?
A The supply of coffee is likely to be inelastic in the short run.
B Economies of scale can lead to lower prices.
C Inferior goods have a negative income elasticity of demand.
D The government was wrong to introduce university tuition fees.
8 The diagram below shows the demand and supply curves for milk, where P1 is the initial equilibrium price.
shows the demand and supply curves for milk, where P1 is the initial equilibrium price.
The increase in price from P1 to P2 is most likely to be a result of
A an increase in milk production costs and a decrease in the price of complementary goods to milk.
B a successful advertising campaign for a milk substitute and a tax on milk.
C a decrease in the population and an increase in the subsidy on milk.
D a decrease in wages paid to all workers, including farm workers.
9 An external benefit is most likely to arise when
A firms are able to reduce their costs of production by undertaking research and development.
B a reduction in the tax on profits increases the amount of money firms have available for investment.
C the government subsidises commuter rail services in order to reduce road congestion.
D a firm is able to dispose of waste products into rivers free of charge.
10 Government failure occurs when
A government intervention leads to a net welfare loss compared to the free market solution.
B social costs in a market are greater than social benefits.
C the government fails to intervene in the market.
D externalities exist in a market.
11 The table below shows benefits and costs of a new motorway.

From the table it can be concluded that
A the social costs are £80 million.
B the social costs are less than the private costs.
C the social costs are less than the social benefits.
D social benefits are £20 million.
12 Price elasticity of supply for games consoles is likely to be higher
A the higher the income of consumers.
B in the long term than in the short term.
C the slower the rate of change in technological progress.
D the less firms are able to switch resources from the production of other goods into the production of games consoles.
13 All other things being equal, if strawberries and cream are complementary goods, a fall in the price of strawberries will
A shift the demand curve for strawberries to the right.
B cause a movement along the demand curve for cream.
C cause a fall in the price of cream.
D shift the demand curve for cream to the right.
14 The supply and demand diagram below relates to the market for a merit good.
The demand curve for the merit good shifts from D1 to D2, raising the market price from P1 to P2.
To reduce the price back to P1, the government could introduce a
A minimum price of OP1 per unit.
B subsidy of P1P2 per unit.
C subsidy of EF per unit.
D subsidy of GH per unit.
15 In a market economy, the market mechanism can achieve all the following except
A signalling changes in consumer tastes.
B causing supply to respond to changes in demand.
C eliminating excess supply and demand.
D ensuring a fair distribution of all types of good.
Answer:
1. B 2. A 3. D 4. B 5. B 6. A 7. D 8. B
9. C 10. A 11. C 12. B 13. D 14. C 15. D
A The imposition of a tax on the good
B A new supplier entering the market
C A rise in firms’ wage costs
D A rise in the price of the good
2 Which one of the following is an example of market failure?
A Prices do not reflect the full social costs of production.
B Prices rise so that consumers cannot afford to buy all the goods that they used to purchase.
C Demand falls so that firms have to make workers redundant.
D A firm goes out of business because it cannot find a market for its products.
3 In August 2000 the World Health Organisation said that a 10% increase in cigarette prices worldwide would reduce consumption by 4% in high-income countries and by 8% in low-income countries.
The above statement suggests that
A smokers in high-income countries are twice as addicted as those in low-income countries.
B demand for cigarettes is price elastic in both low-income and high-income countries.
C income elasticity of demand for cigarettes is higher in low-income than in high-income countries.
D price elasticity of demand for cigarettes is negative in both high-income and low-income countries.
4 The diagram below shows the production possibility boundaries for Countries X and Y respectively.

The opportunity cost of cars in terms of bicycles
A is greater for Country X than for Country Y.
B is greater for Country Y than for Country X.
C increases as more cars are produced.
D increases as more bicycles are produced.
5 The National Grid is a system which distributes electricity throughout Britain. It is currently a monopoly. A possible advantage of this monopoly position to electricity customers is that
A a lack of competition in the electricity distribution industry encourages lower prices.
B the monopolist is able to offer lower prices to customers because it can exploit economies of scale.
C by charging high prices, the monopolist is able to ensure an efficient allocation of resources.
D there will be no need for innovation and invention in the electricity distribution industry and so customers can enjoy lower prices.
6 To benefit from specialisation, it is necessary
A to have an efficient means of exchanging goods and services.
B for labour productivity to be high.
C for the production possibility boundary of the economy to be moving outwards over time.
D for significant economies of scale to be gained in all industries.
7 Which one of the following statements involves a value judgement?
A The supply of coffee is likely to be inelastic in the short run.
B Economies of scale can lead to lower prices.
C Inferior goods have a negative income elasticity of demand.
D The government was wrong to introduce university tuition fees.
8 The diagram below
 shows the demand and supply curves for milk, where P1 is the initial equilibrium price.
shows the demand and supply curves for milk, where P1 is the initial equilibrium price.The increase in price from P1 to P2 is most likely to be a result of
A an increase in milk production costs and a decrease in the price of complementary goods to milk.
B a successful advertising campaign for a milk substitute and a tax on milk.
C a decrease in the population and an increase in the subsidy on milk.
D a decrease in wages paid to all workers, including farm workers.
9 An external benefit is most likely to arise when
A firms are able to reduce their costs of production by undertaking research and development.
B a reduction in the tax on profits increases the amount of money firms have available for investment.
C the government subsidises commuter rail services in order to reduce road congestion.
D a firm is able to dispose of waste products into rivers free of charge.
10 Government failure occurs when
A government intervention leads to a net welfare loss compared to the free market solution.
B social costs in a market are greater than social benefits.
C the government fails to intervene in the market.
D externalities exist in a market.
11 The table below shows benefits and costs of a new motorway.

From the table it can be concluded that
A the social costs are £80 million.
B the social costs are less than the private costs.
C the social costs are less than the social benefits.
D social benefits are £20 million.
12 Price elasticity of supply for games consoles is likely to be higher
A the higher the income of consumers.
B in the long term than in the short term.
C the slower the rate of change in technological progress.
D the less firms are able to switch resources from the production of other goods into the production of games consoles.
13 All other things being equal, if strawberries and cream are complementary goods, a fall in the price of strawberries will
A shift the demand curve for strawberries to the right.
B cause a movement along the demand curve for cream.
C cause a fall in the price of cream.
D shift the demand curve for cream to the right.
14 The supply and demand diagram below relates to the market for a merit good.

The demand curve for the merit good shifts from D1 to D2, raising the market price from P1 to P2.
To reduce the price back to P1, the government could introduce a
A minimum price of OP1 per unit.
B subsidy of P1P2 per unit.
C subsidy of EF per unit.
D subsidy of GH per unit.
15 In a market economy, the market mechanism can achieve all the following except
A signalling changes in consumer tastes.
B causing supply to respond to changes in demand.
C eliminating excess supply and demand.
D ensuring a fair distribution of all types of good.
Answer:
1. B 2. A 3. D 4. B 5. B 6. A 7. D 8. B
9. C 10. A 11. C 12. B 13. D 14. C 15. D